Transactions & Concurrency
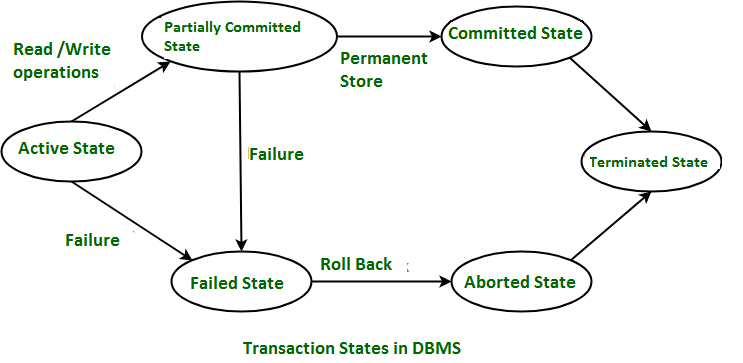
The transaction is a single logical unit that accesses and modifies the contents of the database. Transactions access data using read and write operations. Transaction is a single operation of processing that can have many operations. Transaction is needed when more than one user wants to access same database. Transaction has ACID properties.
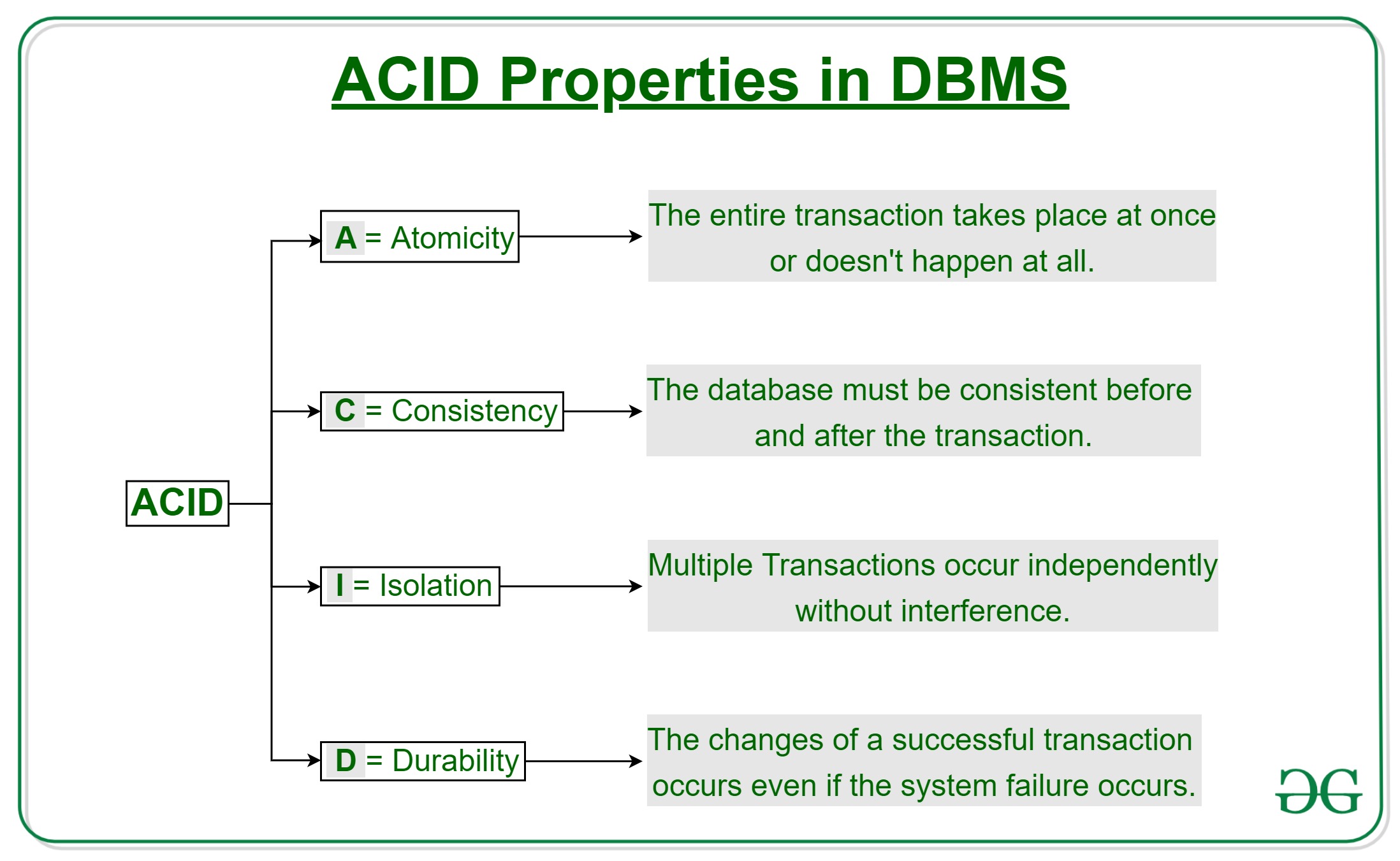
ACID Properties of Transaction:
ACID stands for Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation and Durability
Atomicity: All the operations in a transaction are considered to be atomic and as one unit. If system fails or any read/write conflicts occur during transaction the system needs to revert back to its previous state. Atomicity is maintained by the Transaction Management Component.
Consistency: Every transaction should lead to database connection from one valid state to other valid state. If system fails because of invalid data while doing an operation revert back the system to its previous state. Consistency is maintained by the Application manager.
Isolation: If multiple transactions are executing on single database, each transaction should be isolated from other transaction. If multiple transactions are performed on single database, operation from any transaction should not interfere with operation in other transaction. Isolation is maintained by the concurrency control manager.
Durability: Durability means the changes made during the transactions should exist after completion of transaction. Changes must be permanent and must not be lost due to any database failure. It is maintained by the recovery manager.
Example:
A has an account with an amount of Rs 150. B has an account with an amount of Rs 50. A is transferring amount Rs 100 to B’s account.
Atomicity: Operations required for transfer are: Deduct amount Rs100 from A’s account. Add amount Rs 100 to B’s account. All operations should be done. If system fails to add amount in B’s account after deducting from A’s account, revert the operation on A’s account.
Consistency: The sum amount in A’s account and B’s account should be same before and after the transaction completes. In the example the sum of both account before and after transaction is Rs 200, which preserves the consistency.
Isolation: If there is any other transaction (let between A and C) is going on, it should not affect the transaction between A and B i.e., both the transactions should be isolated.
Durability: It may happen system gets crashed after the completion of all operations then, after restarting it should preserve all the changes. The amount in A’s and B’s account should be same before and after the system restart.
Last updated